Map of Sykes-Picot Agreement, 1916
A map showing the Russian-French-English secret agreement that carved up the Middle East into future areas of interest.
By Topic
Find content relevant to your specific interests or area of study.
By Type
Choose the format that best suits how you want to engage with the content.
By Language
Access content in the language that best supports your learning.
By Era
Explore content organized by historical period to focus your learning by timeframe.
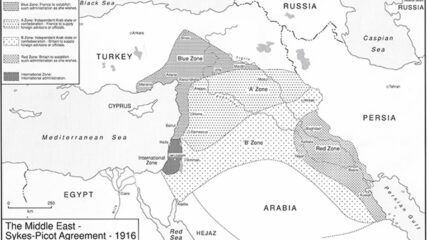
A map showing the Russian-French-English secret agreement that carved up the Middle East into future areas of interest.
Great Britain and France secretly negotiated the Sykes-Picot Agreement in 1916. The two European powers agreed, according to their respective spheres of influence, to divide the Middle East territories previously administered by the Ottoman Empire.

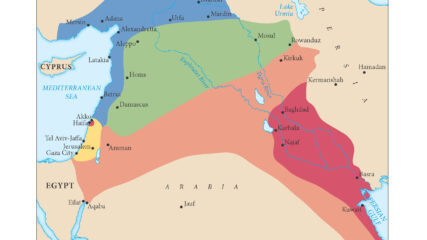
The British and French zones of influence, or mandates, in the eastern Mediterranean region were ratified by the San Remo Agreement in 1920 and approved by the League of Nations in 1922.
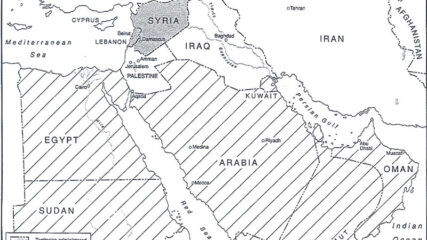
The European agreement that identified the states of the Middle East, 1920.
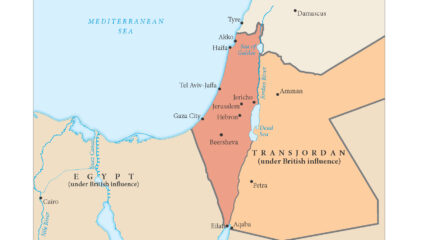
As shown in this map, the British in 1921 separated a new emirate, Transjordan, from what officially became the Mandate for Palestine the next year. The British officially maintained political and military control of both areas until withdrawing in 1948.
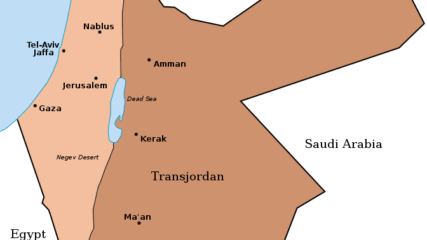
When Britain controlled Palestine, she lopped off 80% of it and assigned it to the Hashemite family leader, Emir Abdullah. It became today’s Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan.
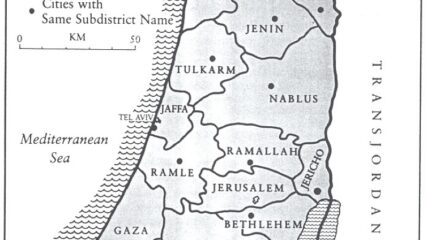
Stein, Kenneth W. The Land Question in Palestine, 1917-1939. North Carolina: University of North Carolina Press, 1984 and 2003. Copyright, Ken Stein and the Center for Israel Education, 2024.

A map shows the partition of Palestine proposed by the Peel Commission in 1937.
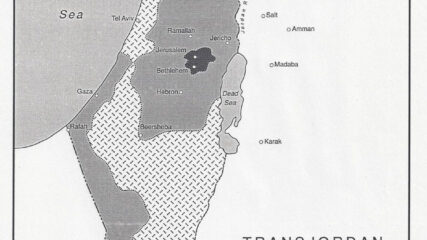
The UN suggested partition of Palestine into Arab and Jewish states with an economic union between them and an internationalization of Jerusalem.
The United Nations General Assembly approved Resolution 181 on Nov. 29, 1947, to divide the British Mandate of Palestine into an Arab state and a Jewish state along the lines in this map, with an international zone around Jerusalem.

The area of Israel expanded and the potential area for a Palestinian Arab state decreased because of the 1948-49 war, Israel’s War of Independence. The Arab rejection of the 1947 U.N. partition plan thus hurt the Arab side, as the maps demonstrate.
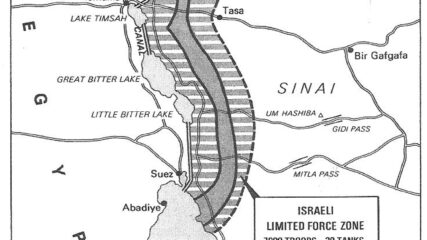
In the aftermath of the 1948 War of Independence, Israel signed armistice agreements with Egypt, Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon. These armistice lines lasted until the immediate aftermath of the June 1967 War. Israel has 1068 kilometers in land borders. Egypt 208 km, Gaza Strip 59 km, Jordan 307 km, Lebanon 81 km, Syria 83 km, and the West Bank 330 km; its Mediterranean coastline 273 km. CIA The World Factbook – Israel

Drafted by Minister of Labor Yigal Allon after the June 1967 war, the plan envisages Israeli retention of a series of settlements and military installations along the Jordan Valley as buffers to a potential Arab land attack from the east.
For Sadat, who had gone to war against Israel three months earlier, securing a military disengagement agreement was important. In addition, diplomatically engaging the US to secure the agreement meant entrenching Washington as a friend of Egypt. The US embraced the opportunity to quell tensions between Israel and Egypt, while squiring Cairo away from decades of Moscow’s embrace. Israel had its POWs returned and slowly tested Sadat’s broader intentions toward Jerusalem.
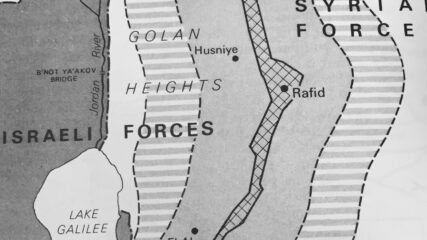
In the last days of the June 1967 War Israel secured a portion of the Syrian Golan Heights, estimated at 1300 sq km or 500 sq mi; Israel forces sit some 40 miles, 60km from Damascus. Before the June War, Israeli villages and populations in the valley were fired upon by Syrian forces from the Heights. In addition to being an important catchment for Jordan River waters which helps supply Israel’s water needs, the heights contain not fully explored hydrocarbon sources. In the northern Heights is Mt. Hermon which has strategic value for observing military movements into southern Lebanon and to Damascus.
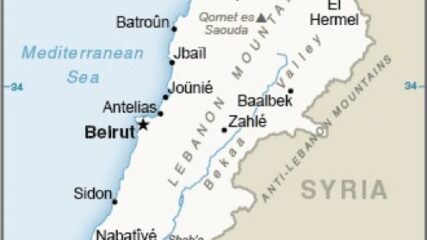
The map includes the Israeli border and the Litani River, which is about 18 miles north of the Israeli-Lebanese border and runs roughly parallel to it. U.N. Security Council Resolution 1701 from 2006 calls for Hezbollah to withdraw north of the Litani.
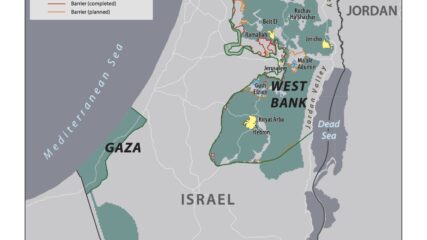
This map shows the State of Palestine as proposed by the Trump plan with features and selected locations from the Washington Institute Settlements and Solutions website.
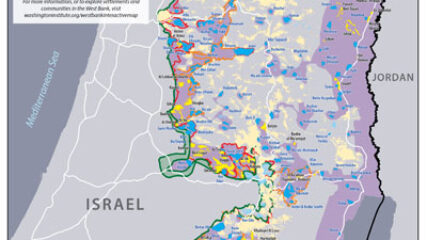
Israeli prime minister Binyamin Netanyahu has repeatedly declared that he will be putting forward his proposal for West Bank annexation as early as July 1. Yet uncertainties about his plans still abound, indicating that this timetable may not be met despite his assertions to the contrary.
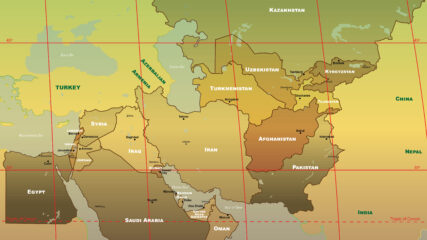
The U.S. military’s Central Command is responsible for an area stretching from Egypt to Pakistan to Kazakhstan, including Israel since September 2021.
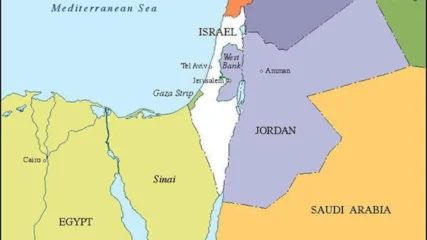
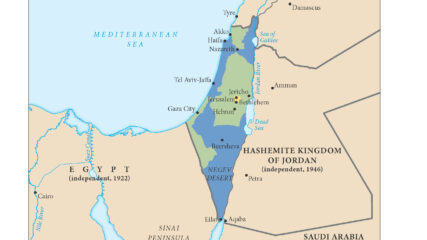
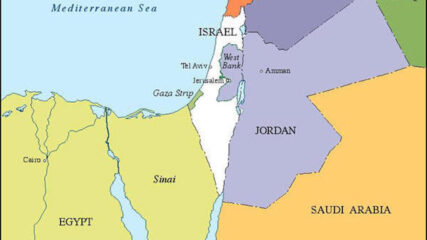
A current map showing the political borders of Israel and its nearest neighbors in the Arab world.
