The maps presented below are only a few that could be used in learning and teaching about Israel and the Middle East.
CIE wishes to thank Aliza Cramer Elias and her team at the Institute for Curriculum Services for allowing CIE to promote the use of the maps that they produced, found here in English and in Spanish.
Diplomacy and war reflect the changing contours of states and borders along the evolution of Israel and the modern Middle East. We wish to thank the Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs for allowing us to use some of their published maps. Others were made for CIE use.
Max Fisher has assembled 40 maps of the Middle East from ancient times to the present, each with a brief introduction. This is a first-rate collection with almost no noticeable bias and with a devotion to accuracy.
In addition, Michael Izady’s collection, the Gulf2000 project, focuses on eight countries of the Persian/Arabian Gulf. Izady also lists other map collections, including the Library of Congress, rich in historical items.
The University of Texas also has a fine collection of Middle East maps, most of them drawn from the public-domain collection created by the CIA.
Israel’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs provides contemporary and historical maps of Israel and its neighborhood.
For Spanish-language maps, please click here.
For Hebrew-language maps, please click here.
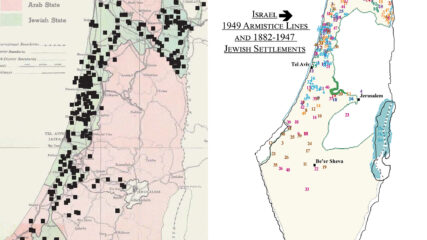
With 20 maps and prose, trace the progression of Jewish physical and demographic growth toward state building from 1882 to 1948 (25,000 to 600,000), with two-thirds in place by 1940.
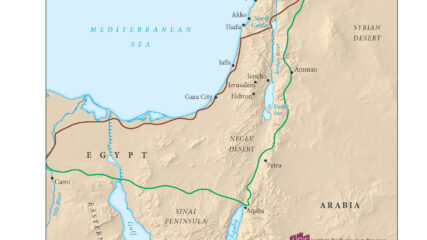
This map shows the Levant, including the Land of Israel, which serves as a bridge linking Africa, Asia and Europe. The map shows ancient trade routes but not political borders before or after World War I.
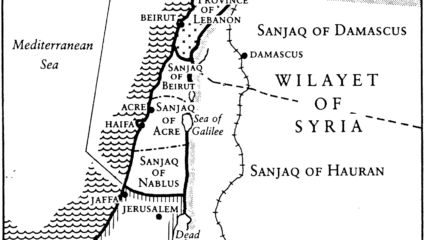
The area of Eretz Yisrael was part of the Ottoman Empire and composed of three large administrative areas without any political identity as a state or part of a state. At times, portions of the area that was later designated as the Palestine Mandate were ruled from Mecca, Damascus, or Baghdad, or in the case of Jerusalem, directly from Istanbul.
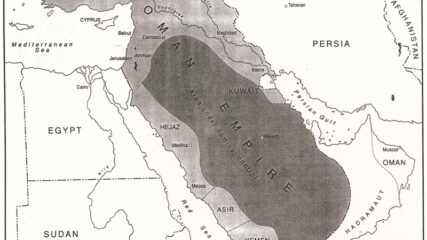
The region prior to the outbreak of World War I. After the war, modern Middle Eastern states had their borders arbitrarily drawn by European powers.
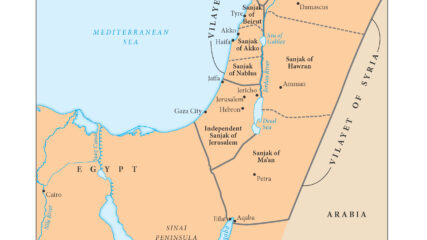
This map shows the Ottoman Empire’s administrative districts before World War I broke out in August 1914 in areas that today are Israel, Gaza, the West Bank, Lebanon, Jordan, Syria and part of Iraq.
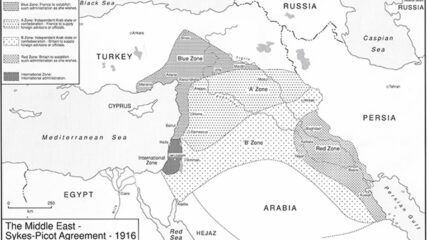
A map showing the Russian-French-English secret agreement that carved up the Middle East into future areas of interest.
Great Britain and France secretly negotiated the Sykes-Picot Agreement in 1916. The two European powers agreed, according to their respective spheres of influence, to divide the Middle East territories previously administered by the Ottoman Empire.

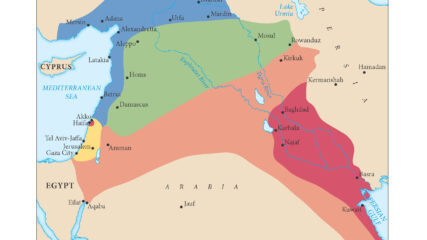
The British and French zones of influence, or mandates, in the eastern Mediterranean region were ratified by the San Remo Agreement in 1920 and approved by the League of Nations in 1922.
The European agreement that identified the states of the Middle East, 1920.
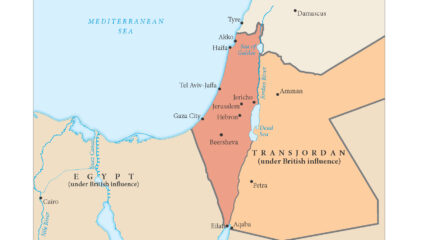
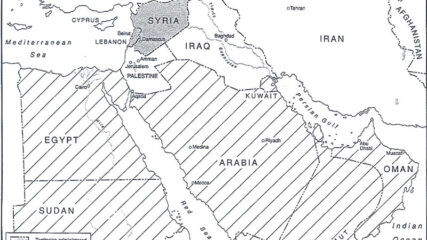
As shown in this map, the British in 1921 separated a new emirate, Transjordan, from what officially became the Mandate for Palestine the next year. The British officially maintained political and military control of both areas until withdrawing in 1948.
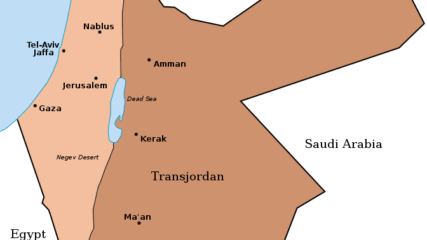
When Britain controlled Palestine, she lopped off 80% of it and assigned it to the Hashemite family leader, Emir Abdullah. It became today’s Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan.
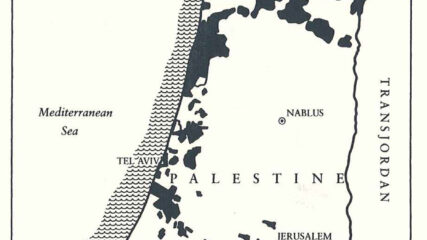
Jewish land acquisition in 1930 mostly in the valley and coastal regions.
Stein, Kenneth W. The Land Question in Palestine, 1917-1939. North Carolina: University of North Carolina Press, 1984 and 2003. Copyright, Ken Stein and the Center for Israel Education, 2024.

A map shows the partition of Palestine proposed by the Peel Commission in 1937.
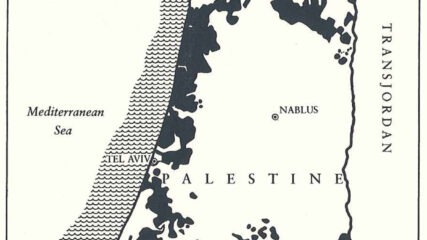
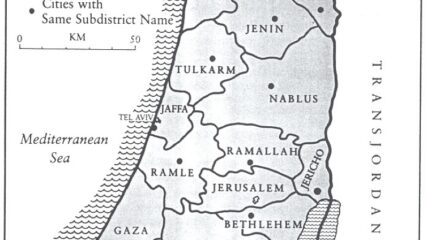
Jewish land acquisition in 1944.
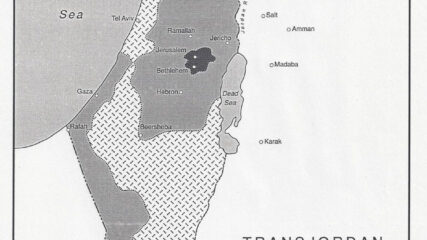
The UN suggested partition of Palestine into Arab and Jewish states with an economic union between them and an internationalization of Jerusalem.
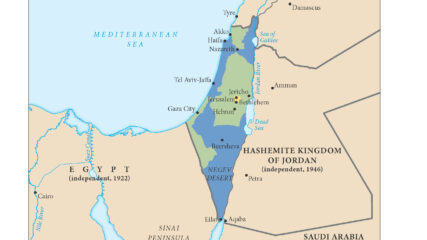
The United Nations General Assembly approved Resolution 181 on Nov. 29, 1947, to divide the British Mandate of Palestine into an Arab state and a Jewish state along the lines in this map, with an international zone around Jerusalem.
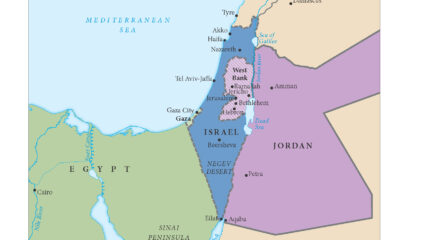
This map shows the territories controlled by Israel, Jordan (including the West Bank(, Lebanon, Syria and Egypt (including the Gaza Strip) at the end of Israel’s War of Independence in 1949. An Arab state was not created in Palestine. Jordan annexed the West Bank, and Egypt maintained administrative control of the Gaza Strip. Israel captured Gaza and the West Bank in the June 1967 war.

The area of Israel expanded and the potential area for a Palestinian Arab state decreased because of the 1948-49 war, Israel’s War of Independence. The Arab rejection of the 1947 U.N. partition plan thus hurt the Arab side, as the maps demonstrate.
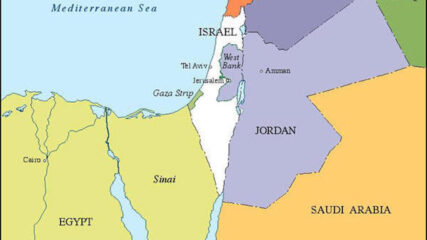
In the aftermath of the 1948 War of Independence, Israel signed armistice agreements with Egypt, Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon. These armistice lines lasted until the immediate aftermath of the June 1967 War. Israel has 1068 kilometers in land borders. Egypt 208 km, Gaza Strip 59 km, Jordan 307 km, Lebanon 81 km, Syria 83 km, and the West Bank 330 km; its Mediterranean coastline 273 km. CIA The World Factbook – Israel
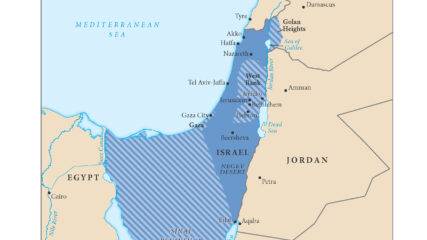
With its six-day victory in the June 1967 war, Israel added the Sinai Peninsula, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights and the West Bank (Judaea and Samaria) to the territory under its control. Israelis moved into all of those areas over the next decade.
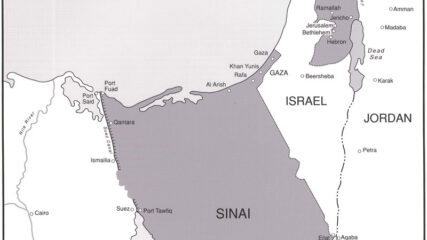
As a result of the June 1967 War, Israel increased its size seven fold to include Eastern Jerusalem, the Golan Heights, the West Bank of the Jordan River, and the Gaza Strip.

Drafted by Minister of Labor Yigal Allon after the June 1967 war, the plan envisages Israeli retention of a series of settlements and military installations along the Jordan Valley as buffers to a potential Arab land attack from the east.
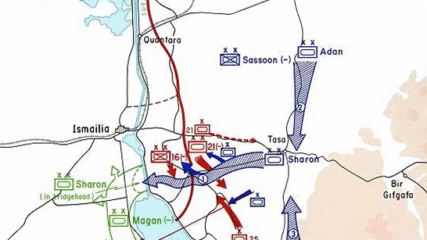
Israel troop crossings with Egyptian counterattacks during the Yom Kippur War (October 1973). Israeli forces were led by Generals Sharon, Aden and Magen. Description of the Israeli Suez Canal crossing, Israel State Archives, October War
























