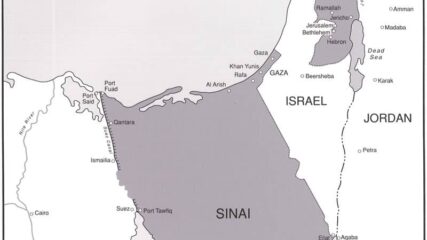
Memorandum of Conversation Between U.S. President Carter and Israeli Foreign Minister Dayan, October 1977CIE+
Common to both the Labor Party and to Begin’s government was a fear that the US would pressure Israel into unwanted concessions and deny Israel its right to sovereign decision-making. It was a concern that Dayan expressed in this October 1977 meeting, and one that he would articulate on several occasions during the Camp David negotiations.