President Ford’s Promises About the Golan Heights, 1975CIE+
President Ford promises that the US will give “weight” to any future Israeli peace agreement with Syria that Israel should remain in the Golan Heights.

President Ford promises that the US will give “weight” to any future Israeli peace agreement with Syria that Israel should remain in the Golan Heights.
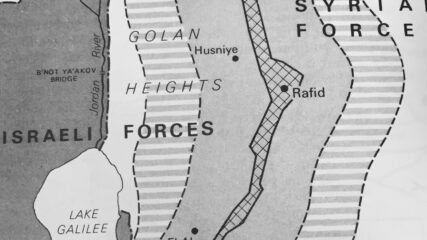
In the last days of the June 1967 War Israel secured a portion of the Syrian Golan Heights, estimated at 1300 sq km or 500 sq mi; Israel forces sit some 40 miles, 60km from Damascus. Before the June War, Israeli villages and populations in the valley were fired upon by Syrian forces from the Heights. In addition to being an important catchment for Jordan River waters which helps supply Israel’s water needs, the heights contain not fully explored hydrocarbon sources. In the northern Heights is Mt. Hermon which has strategic value for observing military movements into southern Lebanon and to Damascus.

On the Golan Heights, Israel agrees to a limited withdrawal, and the United Nations places forces between the Syrian and Israeli armies. With few exceptions this border remains quiet for more than 40 years.
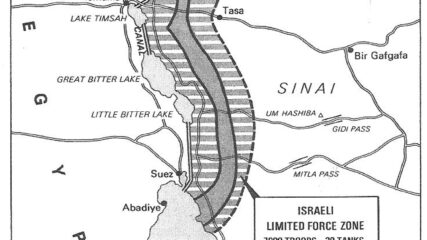
For Sadat, who had gone to war against Israel three months earlier, securing a military disengagement agreement was important. In addition, diplomatically engaging the US to secure the agreement meant entrenching Washington as a friend of Egypt. The US embraced the opportunity to quell tensions between Israel and Egypt, while squiring Cairo away from decades of Moscow’s embrace. Israel had its POWs returned and slowly tested Sadat’s broader intentions toward Jerusalem.

The US promises to implement an Egyptian-Israeli disengagement agreement and have the Suez Canal cleared. Israel sees eventual repopulation of Suez Canal cities as a sign that Egypt will not go to war again soon.

The U.S. mediates an agreement separating forces in Sinai after the October 1973 war. Egyptian and Israeli generals will negotiate additional details.

Henry Kissinger and and Hafez al-Assad meet in Damascus in December 1973 (credit: Agence France-Presse stringer, released by Getty in January 1974). By Ken Stein Sandwiched between the end of the 1973 October Middle East…

U.S. Secretary of State Kissinger failed to persuade Syrian President Assad to attend the December 1973 Geneva Middle East Peace Conference. Assad saw the proposed conference, which it was, a ruse to cover up a “pre-cooked” Israeli-Egyptian arrangement. Assad wanted no part of implicitly supporting any agreement where Israel’s legitimacy might be enhanced.

Proceedings of a conference concluded that while pre-war intelligence was plentiful and accurate, there was a massive U.S. intelligence failure. Misinterpretation layered on top of preconceived notions of Arab military ineptitude and faith in diplomacy formed the core of the failures.

Ken Stein explains in detail how Egyptian and Israeli leaders coached their generals into reaching an understanding on how their troops would be disengaged after the war. On that day, a German-born Egyptian career foreign service officer, Omar Sirry was told to pack his toothbrush and go to meet several Israelis along with other Egyptians at the 101 Kilometer marker for talks.

In the 1970s, US State Department Ambassador Michael Sterner was privy to Sadat’s preference for step-by-step diplomacy PRIOR to the 1973 October War. He is critical of the Carter administration for being too satisfied with only a bilateral Egyptian-Israeli Agreement.

Omar Sirry provides intimate details of the diplomatic aftermath of the October 1973 War, the Kilometer 101 talks, Kissinger’s choreography of the December 1973 Middle East peace conference, and admiration for Sadat as the “modern Egyptian Pharaoh” who was not ever politically passive but took repeated initiatives for Egypt’s benefit.

Ashraf Ghorbal represented Egypt to the US for four years from 1968 to 1972 until Egypt restored diplomatic relations with the US in the wake of the October War. Ghorbal was Sadat’s Ambassador in Washington for 11 years until 1984. He credits Sadat with foresight in setting out and fulfilling his diplomatic objectives; breaking from the USSR, aligning Cairo with the US, harnessing US diplomacy under Kissinger and Carter to secure Sinai’s return to Egyptian sovereignty, and even if that meant signing agreements and recognizing Israel.

June 10, 1992 (Permission to publish this interview granted by Peter Rodman, June 1992) Peter Rodman, member of United States National Security Council Staff and Special Assistant to Henry Kissinger and Brent Scowcroft, August 1969…

Tahsin Bashir served as spokesman for Egypt and for the Arab League in many capacities from 1963 to 1978. He knew Anwar Sadat intimately, revealing that Sadat kept his own counsel while using others to test political and diplomatic options. His long-term goal was to reorient Egypt away from Moscow and obtain Sinai’s return. Sadat cleverly managed others, including Kissinger, Carter and his own advisers.

The October 1973 war broke the logjam over whether diplomacy could unfold to kick off Arab-Israeli negotiations. Sadat used the 1973 war as an engine to harness American horsepower. In that he succeeded because U.S. Secretary of State Kissinger saw Sadat’s leaning to Washington not only as a chance to begin useful negotiations, but also of great significance to weaning the Egyptian president away from Moscow.

In carrying out research in the 1990s for Heroic Diplomacy: Sadat, Kissinger, Carter, Begin and the Quest for Arab-Israeli Peace, Routledge, 1999, I undertook 84 interviews with individuals who participated in the diplomacy.

Egyptian President Sadat colluded with Syrian President Assad to attack Israel on October 6, 1973. Sadat’s objective was not to seek Israel’s destruction but to gain a limited success by crossing the canal. He also sought to engage American diplomacy to generate talks with Israel that would see Israeli withdrawal from Egyptian land Israel secured in the June 1967 War. Sadat took a large gamble by attacking Israel yet he unfolded a negotiating process with Israel that lasted through 1979. He achieved his overarching long-term priority of having Egyptian Sinai returned to Egyptian sovereignty.

With less than three dozen Israeli settlements in the territories taken in the June War, the proposal is not for a vast settlement increase, but for economic, infrastructure, and industrial development of the areas.

October 6, 2023, was the 50th anniversary of the outbreak of the October 1973 war. Six months prior, Egyptian President Sadat sent his national security adviser to meet with Secretary of State Kissinger to determine whether the U.S. would engage Egypt and Israel in serious mediation for a Sinai agreement, or a series of them, all focused on Israeli withdrawal and gradual acceptance of Israel. Kissinger did not take Sadat’s overtures seriously. Would American action then have avoided the October 1973 war? All informed analyses say no.

This volume of the U.S. government’s “Foreign Relations of the United States” series provides foreign policy documents on the Arab-Israeli conflict before, during and after the October 1973 war.

One of Israel’s greatest writers, Natan Alterman, reminded Israel’s accusers in 1969 that well into the 20th century the Palestinians did not even understand themselves as a separate people with a distinctive national identity marking them off from other Arabs. His argument, if framed as a question, might be formulated along these lines: If no one else, not least the Palestinians’ ancestors, saw their distinctive nation in Ottoman Palestine, how can the Zionists be blamed for not seeing one either? Thus, to fault the Zionists for failing to see what was not yet visible to anyone else, including the Palestinians, is to fault them not for suffering from blindness, but for lacking clairvoyance.

Without any consultation with Jerusalem, Israel rejects US proposal for full withdrawal.
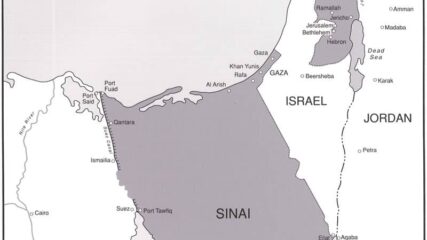
Resolution 242 calls for Israeli withdrawal from unspecified captured territories in return for the right of all states to live in peace. It does not call for a full withdrawal. It is the basis for treaties with Egypt (1979) and Jordan (1994) and for PLO recognition of Israel (1993).