Assembled here are key sources that have shaped the modern Middle East, Zionism and Israel. We have included items that give texture, perspective and opinion to historical context. Many of these sources are mentioned in the Era summaries and contain explanatory introductions.

For more than a century, Arab and Muslim leaders have expressed hatred for Jews, Zionism and Israel, although some have pointed internally for the failures of the Palestinian Arab national movement.

The Israel State Archives’ “The Six Day War Files” includes Cabinet and Security Cabinet meeting transcripts that were classified for 50 years.

Two days after the conclusion of the June 1967 War, Eshkol, recounts the series of events that led to war, the war itself and the immediate aftermath. He reaches out to Arab states for peace seeking a path to peace with her belligerent neighbors. A week later, Israel will quietly messages Cairo and Damascus through the US, hat Israel seeks an end to the conflict. No answers are received.

After the June 1967 war, the Israeli government sent word through the United States to Egypt and Syria seeking to jump-start a peace process. Apparently no response was received.
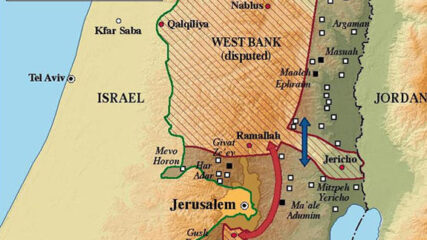
Yigal Allon’s plan for handling the areas captured from Jordan during the just-completed Six-Day War reflects Israel’s previous border vulnerability and seeks a West Bank arrangement that is not a strategic or geographic threat.

Unknown to the Carter administration and one month before it issued the US-Soviet Declaration to convene an international Middle East Peace Conference, Prime Minister Begin tells the cabinet that he learned from the Rumanian president that Sadat wishes to have Israeli and Egyptian representatives meet in secret talks. That bi-lateral Dayan -Tuhami meeting takes place on September 16. Begin refers to advanced drafts of proposed treaties between Israel and each Arab state; he presents details about Rumanian Jewish immigration to Israel.

Five weeks after Egyptian President Anwar Sadat flew to Jerusalem in November 1977, to accelerate Egyptian – Israeli negotiations, Begin brought to President Jimmy Carter, Israel’s response to Sadat’s peace initiative: political autonomy for the Palestinians in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. No Palestinian state was considered.

After the September 1978 Camp David Accords ended, the Carter administration diligently tried but failed to persuade Jordan’s King Hussein to be part of the follow-on negotiations over Palestinian autonomy. Carter felt Hussein was obstructionist; Hussein did not believe in 1978 that the US could halt Israeli settlement building as promised then. Hussein was correct. He also believed that Palestinian Autonomy might have a negative impact on many Palestinians living in his kingdom. Hussein was skeptical of the US capacity to negotiate for his national interests. At the same time, privately, Egypt’s Sadat was not displeased that the Jordanians remained out of favor with the US, and away from any negotiations that would detract from implementation of Israel’s promised full withdrawal from Sinai, per their 1979 Treaty. In 1988, Hussein stepped away from the West Bank’s future; in 1994, Jordan signed a peace treaty with Israel.

The Jordanian king and Israeli Labor Party leaders secretly outline a plan to convene an international conference to move Israeli-Palestinian talks forward through a conference format, but Likud opposition leaders squash the idea.

Jordan’s King Hussein made a strategic decision to disassociate administratively from the West Bank, leaving it to focus Jordanian national identity on only the east bank of the Jordan River. The PLO subsequently negotiated with Israel to rule over some of these lands, as codified in the 1993 Oslo Accords, but no Palestinian state was promised.

Forty-one documents compiled by the Israel State Archives illuminate the negotiations beginning in September 1993 that produced an Israel-Jordan peace treaty in October 1994.

Jordan becomes the second Arab country after Egypt (1979) to sign a peace treaty ending the state of war with Israel. The Treaty addresses boundary demarcations, water sharing, police and security cooperation, environmental issues, border crossings, administration of Muslim holy sites and other issues.

In only the second Knesset address by a U.S. president, Bill Clinton hails the treaty Jordan and Israel signed the previous day as part of a peaceful wave sweeping the region, including the year-old Oslo Accords and soon a likely treaty with Syria.

Abdullah II remains studiously noncommittal in support of Donald Trump’s idea for the U.S. to take over the Gaza Strip, rebuild it and relocate its Palestinian residents to other countries. With Jordan’s strong economic, strategic and defense ties to Washington, no one expected the king to be effusive for Trump’s suggestions for Gaza’s future. Jordan lacks the economic and demographic absorptive capacities and the political interest to take another wave of Palestinians into its territory.














