Assembled here are key sources that have shaped the modern Middle East, Zionism and Israel. We have included items that give texture, perspective and opinion to historical context. Many of these sources are mentioned in the Era summaries and contain explanatory introductions.
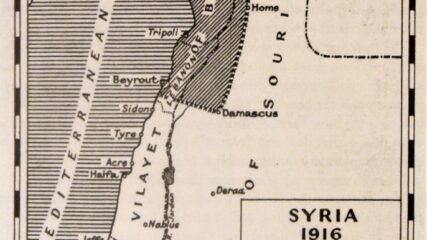
The Sharif of Mecca and Sir Henry McMahon, a British official in Cairo speaking for the Foreign Office, exchange letters about the current war effort against the Turks and the future political status of specific Arab lands in the Ottoman Empire. McMahon says, as he repeats in 1937, that the area of Palestine is excluded from any area to be provided to an Arab leader after World War I. The British instead allow the area of Palestine to develop as a “national home for the Jewish people.”

Britain and France secretly divide the Arab provinces of the reeling Ottoman Empire to meet their own geopolitical interests. They offer no concern for the political aspirations of indigenous populations.

The British Foreign Ministry promises to work toward a Jewish national home in Palestine with no harm to non-Jewish populations or to Jews living elsewhere who might want to support a Jewish home.

A Zionist delegation to the Paris Peace Conference makes an effective, largely successful case for the League of Nations to incorporate a future Jewish national home into the British Mandate for Palestine.
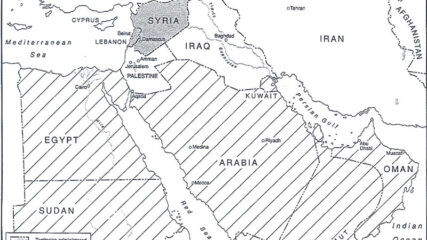
The post-WWI San Remo Conference allocates former Ottoman territories to Britain and France and recognizes Jewish self-determination in Palestine by adopting the language of the Balfour Declaration, decisions the League of Nations confirms two years later.

With intentioned ambiguity, Britain asserts that its goal in Palestine is not to make it wholly Jewish or subordinate the Arab population. Self-determination is not promised. Britain wants to remain an umpire between the communities. Naively, it thinks it can control communal expectations and keep the peace.

International legitimacy is granted to establish a Jewish National Home in Palestine. Rules for its establishment clearly give Jews in Palestine distinct advantages over the local Arab population.

Annual reports to the League of Nations address the status and progress of the British Mandate for Palestine,

Palestine’s High Commissioner Chancellor seeks to halt the Jewish National Home in favor of the Arabs. He fails to overcome the Zionist drive and Arab unwillingness to cooperate with his intentions.

After outbreak of communal violence, the British investigatory committee suggests partition of Palestine, seeking to create two states for two peoples.

Mufti opposes Arab majority state in ten years contrary to wishes of a dozen key other Palestinian leaders. Mufti wants no Jewish political presence in Palestine whatsoever.

Zionist leaders—David Ben-Gurion, Chaim Weizmann and Eliezer Kaplan—learning of the British intent to limit severely the Jewish national home’s growth. Increasingly, they are also aware of the German government’s hostilities towards European Jewry.

Published by the British Administration of Palestine, this summary emphasizes attempts at impartiality in governing the Mandate. It notes that in 1922, the Jewish community already possessed ‘national’ characteristics, while the Arab community’s composition was sociologically and economically divided and to a large degree impoverished by the war.

Earlier in 1947, Great Britain turned the future of the Palestine Mandate over to the newly established United Nations. Then in August 1947, the UN suggested that establishing an Arab and Jewish state with a federal union would be the best solution for the communal unrest there.

The head of Arab League says Palestine may be lost in a confrontation with the Zionists, but emphatically states that war is the Arab’s only option.
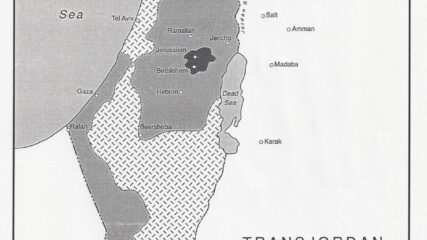
The UN recommended establishing Arab and Jewish states in Palestine, with an international regime for Jerusalem. Zionists were jubilant; Arab states and the Palestinians were indignant and rejected two state solution. No Arab state is established, Israel is in 1948

The Declaration recounts the Jewish connection to the Land of Israel, the birth of Zionism and U.N. recognition of a Jewish state’s legitimacy. It also promises that the state will be a democracy for all its citizens.
This 10-page report, written by the British Colonial and Foreign Office, along with the 1937 Peel (Royal) Commission Report, is one of the two best summaries of the British presence in Palestine. Both are substantial in terms of content, detail and analyses; both were written from Britain’s perspective. Read these along with 1931 Census for Palestine to have a fuller grasp of the politics and the populations that shaped Britain’s Palestine’s administration from 1918-1948
.


















