Assembled here are key sources that have shaped the modern Middle East, Zionism and Israel. We have included items that give texture, perspective and opinion to historical context. Many of these sources are mentioned in the Era summaries and contain explanatory introductions.
The Sharif of Mecca and Sir Henry McMahon, a British official in Cairo speaking for the Foreign Office, exchange letters about the current war effort against the Turks and the future political status of specific Arab lands in the Ottoman Empire. McMahon says, as he repeats in 1937, that the area of Palestine is excluded from any area to be provided to an Arab leader after World War I. The British instead allow the area of Palestine to develop as a “national home for the Jewish people.”

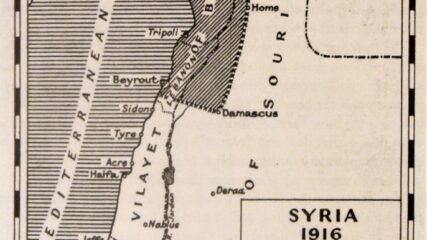
Britain and France secretly divide the Arab provinces of the reeling Ottoman Empire to meet their own geopolitical interests. They offer no concern for the political aspirations of indigenous populations.

Chaim Weizmann advocates for Great Britain to be Palestine’s post-WWI administrator, seeking inclusion of specific territories for its boundaries, six months before Britain issues the Balfour Declaration.

The British Foreign Ministry promises to work toward a Jewish national home in Palestine with no harm to non-Jewish populations or to Jews living elsewhere who might want to support a Jewish home.
Herbert Samuel, soon to serve as Britain’s first high commissioner for Palestine and the only Jew to hold the role, notes reasons for Arab political infighting, the origins of Arab dislike of Zionism, how land sales to Jews generate Arab jealousies, Jewish educational focus and the potential of the region of Palestine to support 4 million people.

With intentioned ambiguity, Britain asserts that its goal in Palestine is not to make it wholly Jewish or subordinate the Arab population. Self-determination is not promised. Britain wants to remain an umpire between the communities. Naively, it thinks it can control communal expectations and keep the peace.

International legitimacy is granted to establish a Jewish National Home in Palestine. Rules for its establishment clearly give Jews in Palestine distinct advantages over the local Arab population.

Palestine’s High Commissioner Chancellor seeks to halt the Jewish National Home in favor of the Arabs. He fails to overcome the Zionist drive and Arab unwillingness to cooperate with his intentions.

Five Arab political parties sent a memorandum of protest to the British asking for a halt to Jewish immigration, a stoppage in Arab land sales to Jews,and a measure of self-determination. The British did not change their policies in these three areas. In 1939, they did severely limit Jewish land purchases and severely curtailed Jewish immigration.

After outbreak of communal violence, the British investigatory committee suggests partition of Palestine, seeking to create two states for two peoples.
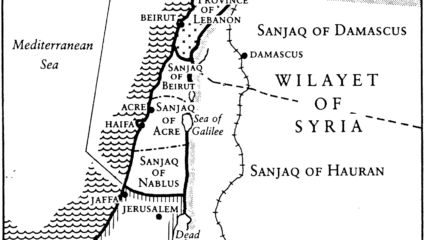
Speculation again abounds whether a two state solution might be a seriously considered outcome to Palestinian-Israeli differences. A long history of its mention but not its implementation persists. Advocacy by external voices persists, but no one seems ready to make the critical political trade-offs required.

Pressure from Arab leaders in states surrounding Palestine, growing instability in the eastern Mediterranean, and a firm opposition voiced by the British High Commissioner in Egypt, Miles Lampson, caused the British to withdraw the idea of resolving the Arab-Zionist conflict with a two-state solution. Instead, heavy restrictions were imposed in 1939 on the growth of the Jewish National home. Coincidently this policy statement is issued, two days after Nazi Germany attacks Jewish, homes, businesses and synagogues, in what came to be known as Kristallnacht.

A British investigation in 1939, before the release of that year’s anti-Jewish White Paper, finds that the area of Palestine was not promised to the Sharif of Mecca during World War I as part of a caliphate.

Zionist leaders—David Ben-Gurion, Chaim Weizmann and Eliezer Kaplan—learning of the British intent to limit severely the Jewish national home’s growth. Increasingly, they are also aware of the German government’s hostilities towards European Jewry.

Over four decades, Winston Churchill’s views on Zionism and Jews varied greatly. Without knowing his long held personal beliefs or the policies he adopted while the Jewish state developed, and only reading this speech, one would not know that he was a political opportunist and certainly not a “Gentile Zionist.”

Before ending his term in 1944 as Palestine’s High Commissioner, Sir Harold MacMichael suggested the partition of Palestine, “Jews and Arabs alike would enjoy the possession of their own respective territories, the former protected by international guarantees for their security, and the latter relieved from fear of further encroachments.”

Moshe Sharett urges the British and Americans to open Palestine to unimpeded Jewish immigration from Europe.

With the British spending local revenue on strategic needs — ports, roads and communication systems — scant funds were devoted to education in the Mandate. Already baked into diasporic habits, the Jewish community raced forward in educating its own in Palestine to inculcate penetrating attachments to Palestine as the Jewish national home. Arab youth literacy ran in place, with separatist education contributing mightily to communal divisions, as occurred simultaneously in the economic and geospatial spheres.

The report of a joint U.S.-British committee on the situation in Palestine and the fate of European Jewish refugees fails to offer solutions the British government will accept but does deliver vital data and insights on the situation between Arabs and Jews in the Land of Israel.

Fearing Communist penetration of the Eastern Mediterranean, Truman at the beginning of the Cold War defines the region as a sphere of US national interest.

Despite an officially anti-Zionist stance, the Soviet Union, hoping to adopt Israel as a Soviet proxy, takes a pragmatic stance and supports the U.N. partition plan of Palestine into separate Arab and Jewish states.

Published by the British Administration of Palestine, this summary emphasizes attempts at impartiality in governing the Mandate. It notes that in 1922, the Jewish community already possessed ‘national’ characteristics, while the Arab community’s composition was sociologically and economically divided and to a large degree impoverished by the war.

Earlier in 1947, Great Britain turned the future of the Palestine Mandate over to the newly established United Nations. Then in August 1947, the UN suggested that establishing an Arab and Jewish state with a federal union would be the best solution for the communal unrest there.
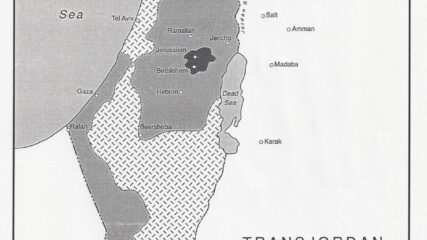
The UN recommended establishing Arab and Jewish states in Palestine, with an international regime for Jerusalem. Zionists were jubilant; Arab states and the Palestinians were indignant and rejected two state solution. No Arab state is established, Israel is in 1948