Assembled here are key sources that have shaped the modern Middle East, Zionism and Israel. We have included items that give texture, perspective and opinion to historical context. Many of these sources are mentioned in the Era summaries and contain explanatory introductions.
Speculation again abounds whether a two state solution might be a seriously considered outcome to Palestinian-Israeli differences. A long history of its mention but not its implementation persists. Advocacy by external voices persists, but no one seems ready to make the critical political trade-offs required.

April 20, 1946 Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry, Report to the United States Government and His Majesty’s Government in the United Kingdom, meeting in Lausanne, Switzerland, 1946. Unsure how to manage Palestine’s future, the British and…

Despite an officially anti-Zionist stance, the Soviet Union, hoping to adopt Israel as a Soviet proxy, takes a pragmatic stance and supports the U.N. partition plan of Palestine into separate Arab and Jewish states.

The Status-Quo Agreement is an understanding reached between David Ben-Gurion, then the chairman of the Jewish Agency Executive, and the religious parties in the period before Israel became a state.

Earlier in 1947, Great Britain turned the future of the Palestine Mandate over to the newly established United Nations. Then in August 1947, the UN suggested that establishing an Arab and Jewish state with a federal union would be the best solution for the communal unrest there.

Loy Henderson, Director of the Office of Near Eastern and African Affairs, U.S. State Department, to U.S. Secretary of State George Marshall
Writing two months before the U.S. voted at the United Nations in favor of Palestine’s partition into Arab and Jewish states, Henderson voices profound dislike for Zionism and a Jewish state. He advocates for cultivating positive relations with Muslim and Arab states. He is one of many at the State Department at the time who saw Zionism as contrary to American national interests.
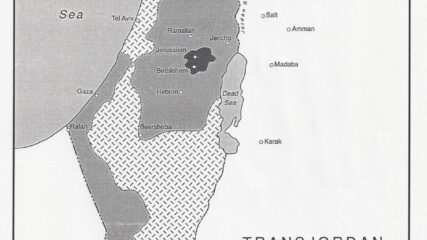
The UN recommended establishing Arab and Jewish states in Palestine, with an international regime for Jerusalem. Zionists were jubilant; Arab states and the Palestinians were indignant and rejected two state solution. No Arab state is established, Israel is in 1948

In March 1948, two months before Israel’s establishment, the US State Department sought to reverse the US vote in favor of partition for the creation of Arab and Jewish states in Palestine.
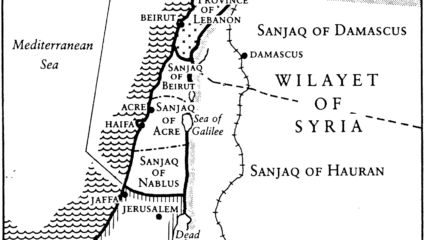
This 10-page report, written by the British Colonial and Foreign Office, along with the 1937 Peel (Royal) Commission Report, is one of the two best summaries of the British presence in Palestine. Both are substantial in terms of content, detail and analyses; both were written from Britain’s perspective. Read these along with 1931 Census for Palestine to have a fuller grasp of the politics and the populations that shaped Britain’s Palestine’s administration from 1918-1948

Subsequent to Israel’s territorial successes from May 1948 forward, U.N. mediator Bernadotte is assassinated after suggesting smaller borders for Israel. He does not mention Palestinian Arabs in his interim report.

The resolution states that refugees “wishing to return to their homes and live at peace (with Israel) should do so or compensation be paid…” Israel opposes the idea because it jeopardizes Israel as a majority Jewish state.

One of four agreements Israel signed in 1949 with Arab neighbors, it does not end “state of war,” between Israel and Arab states. No treaty is signed until 1979.

Upon admission to the U.N., Israeli Foreign Minister Moshe Sharett said, “It was
the consummation of a people’s transition from political anonymity to clear identity, from inferiority to equal status, from mere passive protest to active responsibility, from exclusion to membership in the family of nations.”

This report submitted to the United Nations at the end of 1951 notes that “some one million Jews have become the victims of accelerated antiSemitism” since 1948 in the Muslim countries of the Arab League and North Africa, “communities which have existed for thousands of years.” The report analyzes the situation for Jews overall and explains restrictions and oppressive measures country by country.

A detailed outline is presented of events that led to the June 1967 War.

Following the conclusion of the June 1967 War, the Israeli government sent word to Egypt and Syria seeking peace plan that was intended to jumpstart a peace process with Israel’s belligerent neighbors, Egypt and Syria. The messages were sent through the US, but no response was apparently received.
The Resolution calls for unspecified Israel withdrawal from territories in return for right of all states to live in peace. It does not call for full withdrawal. It is the basis of Egyptian (1979) and Jordanian (1994) Treaties with Israel, and PLO (1993) recognition of Israel.

The October 1973 war broke the logjam over whether diplomacy could unfold to kick off Arab-Israeli negotiations. Sadat used the 1973 war as an engine to harness American horsepower. In that he succeeded because U.S. Secretary of State Kissinger saw Sadat’s leaning to Washington not only as a chance to begin useful negotiations, but also of great significance to weaning the Egyptian president away from Moscow.

On Golan Heights, Israel agrees to limited withdrawal; UN places forces between Syrian and Israeli armies. With few exceptions this border remains almost totally quiet for more than forty years.

Cairo and Jerusalem agree to additional Sinai withdrawals, demilitarized zones, limited force zones and, importantly, placement of US civilians in Sinai to monitor observance of agreement.

Led by USSR and Arab states, Zionism is labeled as racist; the resolution is revoked in 1991.

Carefully sandwiched between Carter’s high-risk presidential visit to Egypt and Israel on March 10, 1979—to solve contentious disagreements between Sadat and Begin—and the Peace Treaty signing on March 26, 1979, his administration gladly votes at the UN to deplore Israeli settlement building; including demographic changes in Jerusalem. After the Peace Treaty signing, until it leaves office in 1981, the Carter administration will continue to barrage Israel with condemnation for settlement building.

This was the second UNSC Resolution within four months supported by the Carter administration condemning Israel’s settlement building in the territories. It too greatly angered the Israeli government and American supporters of Israel.

Showing its public opposition to Israeli actions in the lands taken in the June 1967 war, an area that the Carter Administration
wanted reserved for Palestinian self-rule, it ‘strongly deplores’ Israel’s settlement policies. Passage of the resolution three weeks
prior to the New York and Connecticut presidential primaries, cause many Jewish voters to vote in favor of Ted Kennedy
and not for Carter, helping to splinter the Democratic Party.




















