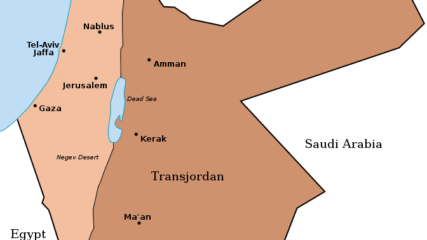
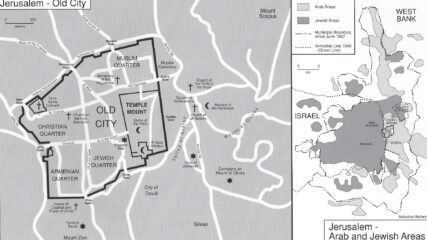
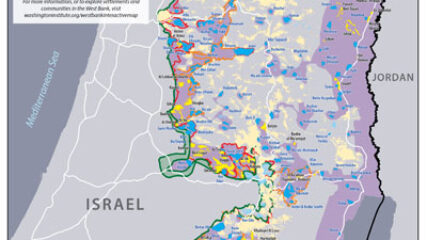
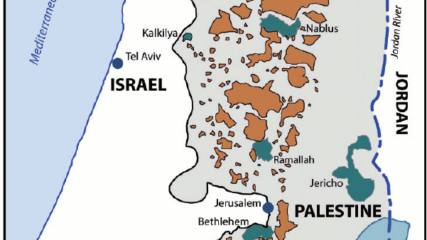
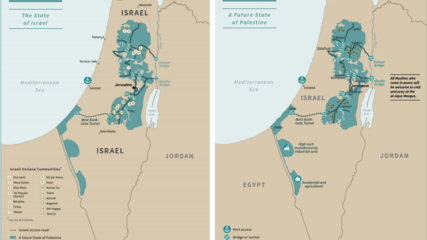
Elaykim Rubinstein, “The Players of Camp David – An insider Israeli view on the personalities and ideas that drove the history-making Camp David Accords,” Cairo Review, Winter 2019.
Introduction With an extraordinary legaI mind and life of civil service to the state of Israel, Rubinstein served as an estimable Supreme Court Judge, as legal adviser during the Egyptian -Israeli negotiations, worked closely with…